Release Inspections and Testing for Categories 2 and 3.
Category 2:
- Must be prepared in a cleanroom suite
- May be assigned a BUD of >12 hours at controlled room temperature or >24 hours if refrigerated
Category 3:
- Have additional requirements that must be met at all times
- May be assigned a BUD longer than established for Category 2 CSPs, up to 180 days
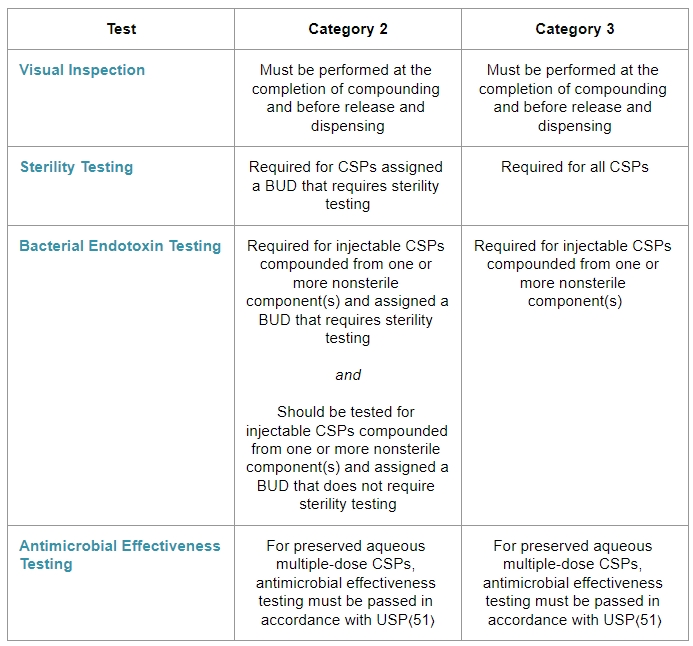
Visual Inspection:
- This determines whether the physical appearance of the CSP is as expected (e.g. free of inappropriate visible particulates or other foreign matter, discoloration, or other defects).
- This confirms the CSP and its labeling match the prescription or medication order.
- This also includes visual inspection of container closure integrity (e.g. checking for leakage, cracks in the container, or improper seals).
Sterility Testing:
- This qualitative test is applied to substances, preparations, or articles required to be sterile. A satisfactory result indicates that no contaminating microorganism has been found in the sample examined under the conditions of the test.
- Method Suitability is required for USP <71> citation.
- An appropriate sample volume of a product lot is filtered or directly inoculated into two microbial growth medias.
- After an appropriate incubation period, the sample is observed for turbidity.
- After the sample has completed testing, a Certificate of Analysis (COA) is issued stating a Pass or Fail result.
Rapid Sterility Testing:
- If an alternative method is used for sterility testing, the method must be validated (see USP <1223>) and demonstrated to be suitable for that CSP formulation.
- Where USP <71> requires between 14 and 18 days of incubation before a final test result, a rapid sterility test result can be generated after only 6 days of incubation.
- This Celsis method can test all sample types including solutions, oil, and suspensions.
- Method Suitability is required.
- An appropriate sample volume of a product lot is filtered or directly inoculated into two microbial growth medias.
- After an appropriate incubation period, an analysis on the media is performed to detect microbial growth.
- After the sample has completed testing, a Certificate of Analysis (COA) is issued stating a Pass or Fail result.
Bacterial Endotoxin Testing:
- The USP <85> Bacterial Endotoxins Test (BET) is a quantitative test to detect or quantify endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria using lysate derived from horseshoe crabs.
- With a kinetic turbidimetric method, a small amount of sample is prepared via serial dilution, along with any necessary additional reagents to overcome enhancement or inhibition effects.
- The prepared sample is transferred to a 96-well plate, and placed into a plate reader.
- Over the course of approximately an hour, the reader examines the wells for a reaction between the lysate and any endotoxin in the product samples.
- Based on either a lack of reaction, or the time taken to observe a reaction, the system calculates a quantitative result based on the sample preparation.
- At the completion of the test, a numerical value is given and reported on a Certificate of Analysis (COA).
- A comparison between the test result and the endotoxin limit for a sample determines whether the test is a Pass or Fail result.
Antimicrobial Effectiveness Testing:
- USP <51> Antimicrobial Effectiveness must be demonstrated for aqueous-based, multiple-dose topical, and oral dosage forms, and for other dosage forms such as ophthalmic, otic, nasal, irrigation, and dialysis fluids.
- In addition, whether inherent in the product or produced because of adding an antimicrobial preservative, antimicrobial effectiveness must be demonstrated for all injections packaged in multiple-dose containers or for other products containing antimicrobial preservatives.
- For this test, aqueous is defined as a water activity of more than 0.6.
- Method Suitability is required for USP <51> citation.
- Separate volumes of product sample are inoculated with high CFU counts of 5 different representative challenge organisms.
- Depending on which of the four categories in the chapter a product falls into, petri plates are prepared with growth media and a sample of the inoculated product at specific intervals over a 28-day period.
- At each of the plating intervals, a CFU count is obtained and compared against the criteria in the chapter.
- At the conclusion of the 28-day incubation and final plating, a Pass or Fail result is reported on a Certificate of Analysis (COA), depending on whether the product met the criteria in the chapter at each plating interval.
